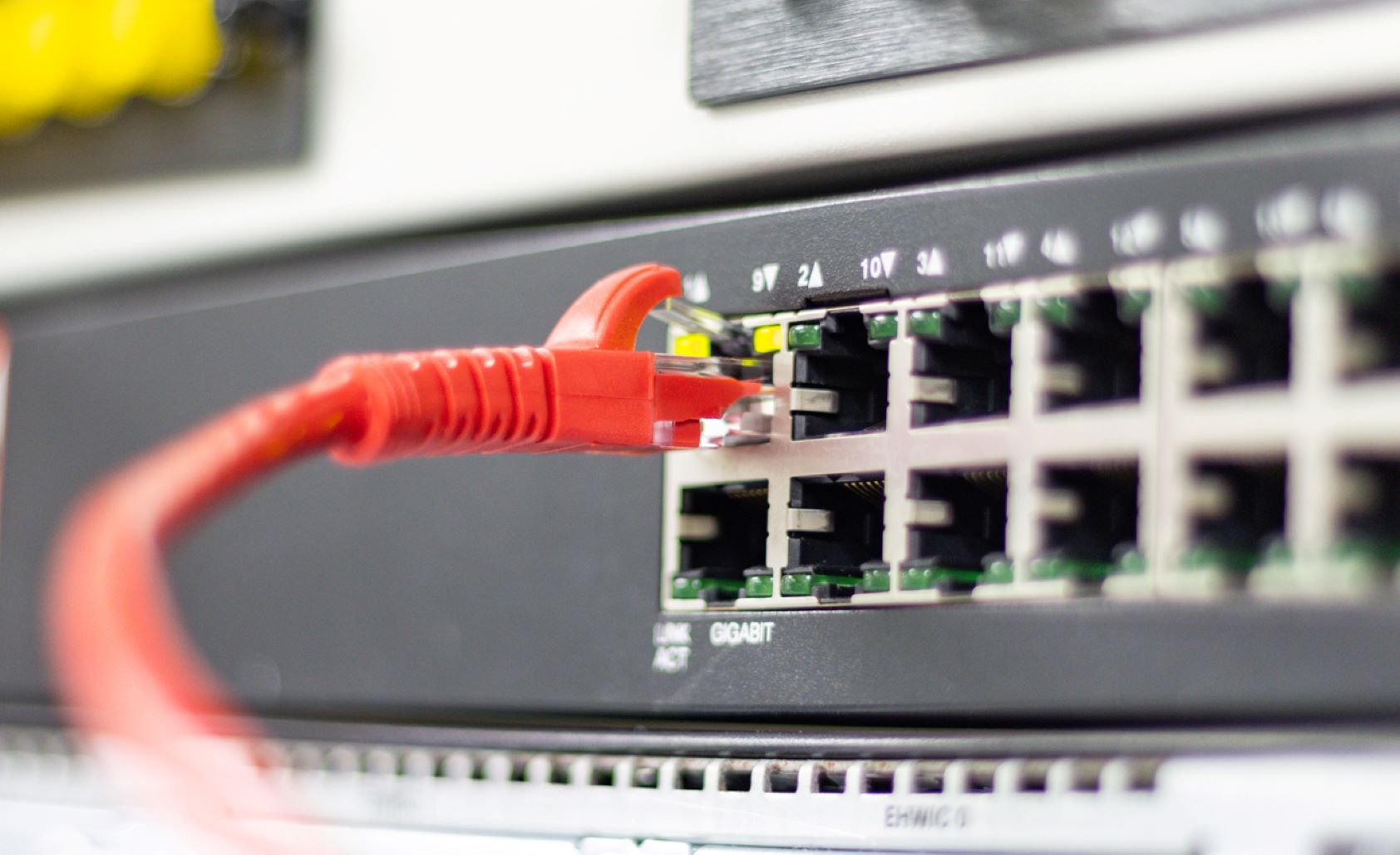
Ethernet is a widely utilized network communication protocol that seamlessly connects various network appliances, switches, and routers. It caters to both wired and wireless networks, including local area networks (LAN) and wide area networks (WAN). The evolution of Ethernet technology has been driven by the imperative need for system compatibility, network security, reliability, and increased bandwidth.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the distinctions between Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet, empowering you to confidently select the most suitable Ethernet data protocol for your specific requirements.
Fast Ethernet
Initially standardized in the mid-80s as IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has continually improved in terms of speed and dependability. Standard Ethernet speeds started at around 10 megabits per second and later reached up to 15 megabits per second.
Fast Ethernet, introduced in 1995 as IEEE 802.3u, was developed to enhance network and device speeds compared to standard Ethernet. It offered consistent data transmission at speeds exceeding 100 megabits per second. Fast Ethernet works with 100 Base T networks and is also compatible with 10 Base T networks. This compatibility allows users to enjoy faster Ethernet speeds (provided they have compatible switches) without completely upgrading their network infrastructure.
Compared to standard Ethernet, Fast Ethernet offers transmission speeds at least ten times faster. This makes it ideal for maintaining reliable connections to high-speed servers, eliminating bandwidth bottlenecks in network systems with multiple IP video cameras and IoT devices, and supporting complex networks running multiple software packages that demand high bandwidth simultaneously.
Fast Ethernet devices can utilize unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cabling, such as Category 5 and higher-rated cables. It's important to note that UTP cabling has a maximum length of 100 meters and may have limited bandwidth capacity.
For enhanced distance range and greater bandwidth capacity, it is highly recommended to use fiber optic transmission instead of UTP cabling. This enables Fast Ethernet devices to fully leverage their capabilities.
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet has been at the forefront of Ethernet standards since its inception in 1999 as IEEE 802.3ab and in 2004 as IEEE 802.3ah. With its ability to provide uniform standards for network transmission at 1000 megabits per second or 1 gigabit per second, Gigabit Ethernet has revolutionized data transfer.
The initial IEEE 802.3ab standard laid the foundation for Gigabit Ethernet's wide-ranging applications, particularly within 1000 Base T networks. This standard also allowed the utilization of existing UTP cabling, making it a cost-effective solution for both industry and desktop users.
In addition, the subsequent IEEE 802.3ah standard paved the way for further advancements in Gigabit Ethernet. It introduced protocols such as 1000 Base LX10 and 1000 Base BX10, enabling multi-mode fiber and fiber optic transmissions.
In terms of performance, Gigabit Ethernet far surpasses Fast Ethernet. While a Fast Ethernet switch can transfer data packets at a rate of 10 megabits per second, a Gigabit Ethernet switch operates at speeds approximately 100 times faster, reaching up to one gigabit per second. This enhanced speed readily meets the demands of modern networks, accommodating multiple bandwidth-intensive devices and enabling seamless video streaming through broadband internet connections.
The applications of Gigabit Ethernet are wide-ranging. From managing data transfer between IP security cameras and network appliances to supporting high-quality video and signal transfer between home servers and high-definition televisions and monitors, gigabit switches play a vital role in various scenarios.
Gigabit Ethernet has transformed network capabilities and is a crucial component in meeting the ever-increasing demands of modern data transfer.
Choosing Between Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet
When considering the most suitable Ethernet data protocol for your operations, both users and organizations must carefully evaluate their options. For smaller operations, Fast Ethernet may be a cost-effective solution to meet their network needs.
However, with the growing demand for high-quality IP surveillance cameras and on-demand video streaming, incorporating Gigabit Ethernet devices can offer significant benefits. It is crucial to assess various factors such as the current network system, available bandwidth, operational requirements, future network configuration, desired upgrades, and facility limitations when selecting the appropriate Ethernet data protocol. By doing so, you can ensure a reliable and efficient network infrastructure that aligns with your specific needs.
Comparing Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet:
When comparing the two options, it is important to consider the following key differences:
- Cost: Fast Ethernet is a more cost-effective choice compared to Gigabit Ethernet
- Configuration: Fast Ethernet offers simpler configuration and management compared to Gigabit Ethernet
- Compatibility: Fast Ethernet is compatible with standard network systems and can support them effectively
- Applicability: Unlike Gigabit Ethernet, Fast Ethernet does not require specifically designed network appliances and devices
- Scalability: Gigabit Ethernet provides greater scalability and can be used in residential, commercial, and large industrial settings
- Speed: Gigabit Ethernet offers a significant speed advantage, being 100 times faster than Fast Ethernet
- Space: Gigabit Ethernet requires smaller hardware and less cabling, resulting in more available physical space
- Distance: Gigabit Ethernet has a longer coverage range, reaching up to 70 km compared to Fast Ethernet's 10 km
- Virtual Networks: Gigabit Ethernet's high bandwidth potential enables easy configuration and management of virtual networks
Still Deciding Between the Two?
Whatever your security requirements, meet them with acre security.
Looking for a custom security solution? Simply tell us your requirements and we’ll connect you with the perfect reseller or installer from our global partner network.
Contact us to start your journey to a safer future with acre security.